Hepatitis C – Early Signs, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Hepatitis C is a condition of the liver caused by the Hepatitis C virus. The disease could range from mild to severe and be short term or last for one’s lifetime. Hepatitis, if left untreated, can also cause liver cancer. Hepatitis C is characterized by the inflammation of the liver and is transmitted through body fluids like blood and semen. It is much easier to transmit hepatitis C through blood (blood transfusions, tattooing, and such) than through sexual contact or childbirth. The condition is treated using antiviral medication to eradicate the virus.
Early warning signs of hepatitis C
The symptoms of hepatitis C are classified based on whether the condition is acute or chronic.
Acute hepatitis C
Acute hepatitis C only affects a small fraction of the patients diagnosed with hepatitis C. The condition is mild, and patients recover quickly in such cases. The early warning symptoms of acute hepatitis C are:
- Joint pain
- Loss of appetite
- Slight fever
- Nausea
- Fatigue and weakness
- Abdominal pain
- Jaundice (yellowing of the eyes and skin)
Chronic hepatitis C
Chronic hepatitis C is a long-term version of the disease, and the symptoms for this type may not appear until the condition progresses. Some early warning symptoms of chronic hepatitis C are:
- Mild fatigue
- Vaguely feeling unwell or uneasy
- Alcohol intolerance
- Serious complications of the liver like liver cancer, liver failure, fibrosis, and cirrhosis as a result of chronic hepatitis C, which may not show up until the disease has progressed to severe stages
- Joint pain, mostly in the hands and wrists
- Difficulty in concentration and poor memory, which can be treated with antiviral therapy
- Sharp pain in the liver
- Upper abdominal pain that can eventually spread throughout the stomach
- Muscle weakness
- Skin irritation
- Dry eyes
- Irritable bowel and bladder
One should not immediately assume that the symptoms are related to hepatitis C, but if one experiences these symptoms for a prolonged period, consulting a doctor for further examination is advisable.
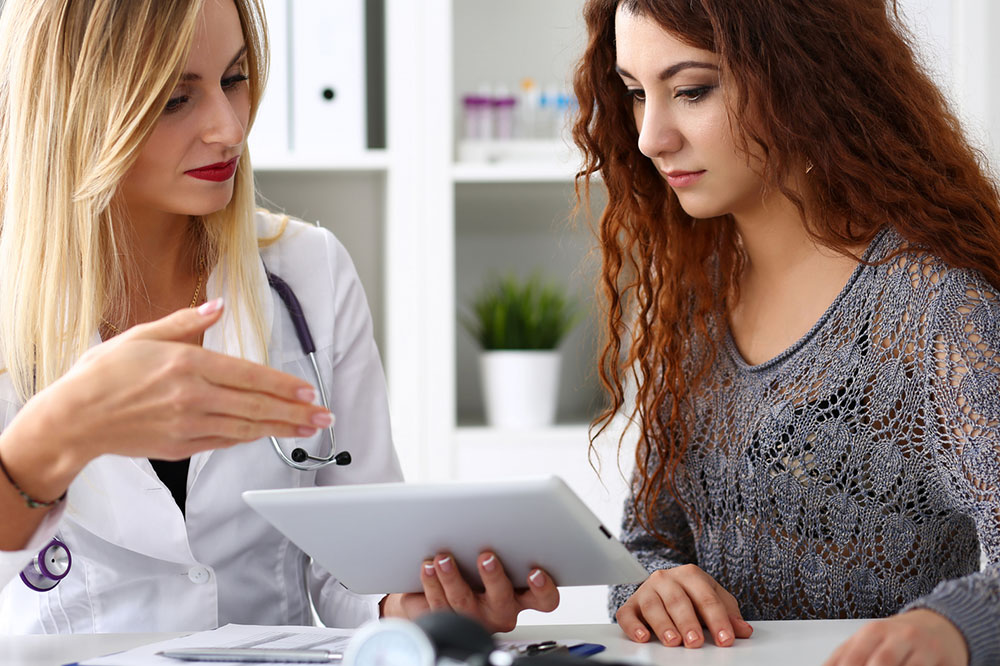
Diagnosis
After suspecting the presence of the Hepatitis C virus in the body, a doctor may draw blood to test it for the same. After the diagnosis is confirmed, further tests are prescribed to examine the extent of liver damage due to the disease. A liver biopsy is a surgical procedure to remove a small liver sample to help a doctor ascertain the progression of the disease.
Treatment
Hepatitis C is mostly treated with antiviral medication over a period of 12 weeks. The type of treatment depends on factors like the genotype of the virus, the degree of liver damage, and the history of one’s treatment for hepatitis C. Two medicines used for the treatment are pegylated interferon and Ribavirin, but recent studies have produced a more efficient and reliable treatment through DAAs. These are tablets may be prescribed in combination with other medications or on their own.