Symptoms and Treatments for Overactive Bladder
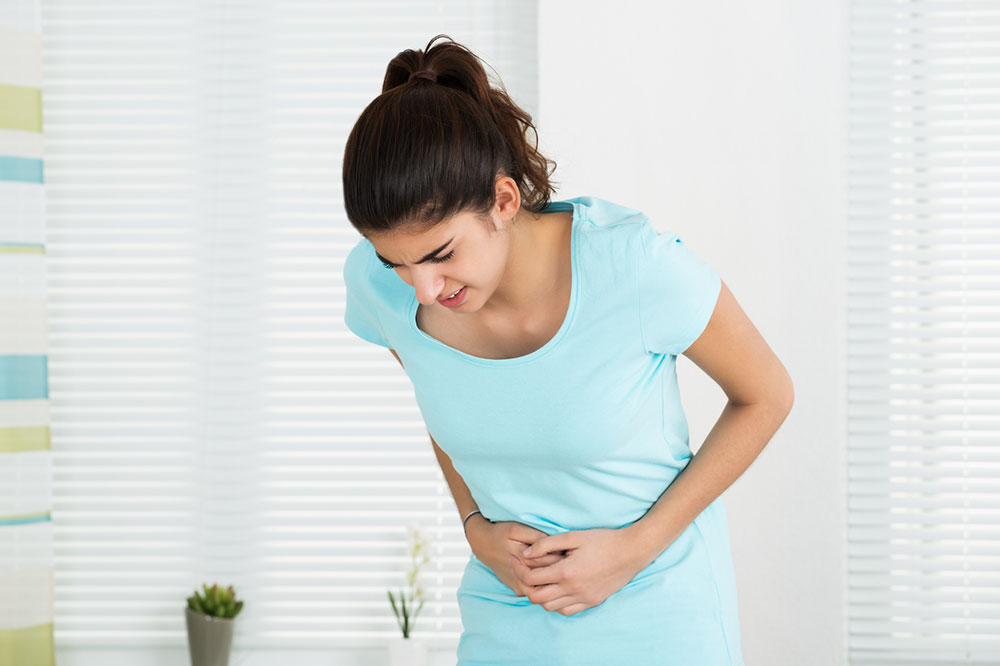
An overactive bladder is a condition wherein one feels the sudden and persistent need to urinate. This condition mostly affects women but may, in rare cases, also affect men. The risk factors of developing an overactive bladder are an enlarged prostate, diabetes, and aging. The need to urinate can be quite hard to control and sometimes leads to incontinence, resulting in embarrassment and mental trauma. Overactive bladder is quite a common condition that affects a lot of people. It is, however, treatable within a matter of months in most cases. Given below are the symptoms of an overactive bladder, along with treatment methods.
Symptoms of overactive bladder
- You experience a sudden urge to urinate that is hard to hold in.
- You experience nocturia, which is when a person wakes up multiple times in one night to urinate.
- Frequent and sudden urination for over 8 times in a single day.
- You experience incontinence, which is the unintentional loss of urine right after getting the urge to urgently urinate.
Treatment for overactive bladder
Behavioral therapy
- Pelvic floor exercises
Kegel exercises are known to strengthen your urinary sphincter and pelvic floor muscles. This can help reduce the bladder’s involuntary contractions. - Biofeedback
In this procedure, you’ll be connected to sensors that measure information received from your body. It then determines the changes that should be made to improve the ability to suppress feelings of urgency. - Healthy weight
Maintain a healthy weight, exercise well, and eat a balanced diet. This helps patients with stress urinary incontinence. - Intermittent catheter
If the case of overactive bladder is particularly severe, you can use a catheter to periodically empty your bladder.
Medication
For women post menopause, vaginal estrogen therapy can be of great help to strengthen muscles and tissues in the pelvic region. It comes in the form of a cream, tablet, and ring. Additionally, there are some other oral medications that can help with an overactive bladder. These must not be taken without a prescription from the doctor as there might lead to a few side effects such as dry eyes, dry mouth, constipation, etc.
Bladder injections
Botox is a protein derived from a bacteria and can be directly injected in small doses into the bladder tissues to suppress incontinence. The effects last over six months but repetitive doses are required.
Nerve stimulation
This treatment method helps to regulate the nerve impulses to a patient’s bladder, consequently helping to improve the symptoms of overactive bladder. A thin wire is placed near the tailbone, close to the sacral nerves. Electric impulses to the bladder can be controlled by a handheld device from outside. If the results are positive, a permanent pulse generator is implanted surgically to regulate the nerve rhythm.
Surgery
If the overactive bladder condition is extremely advanced and the symptoms are bad, surgery is recommended. The procedures include the following:
- To increase bladder capacity: Pieces of your bowel are taken to replace a part of your bladder surgically. However, this procedure may result in you depending on a catheter for the rest of your life.
- Bladder removal: This procedure must be used as a last resort. Here, the entire bladder is removed and a new replacement bladder is surgically reconstructed. Alternatively, an opening can be made in the body and a bag can be attached there to collect urine.